Shein: A Case Study in Fast Fashion Production
Related Articles: Shein: A Case Study in Fast Fashion Production
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Shein: A Case Study in Fast Fashion Production. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Shein: A Case Study in Fast Fashion Production

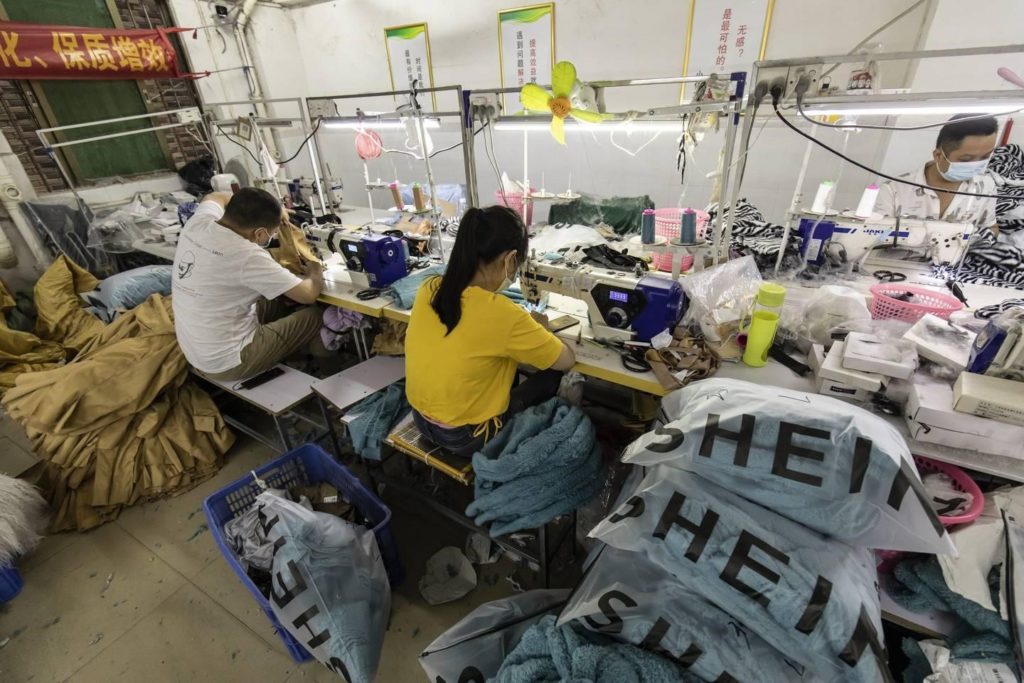
Shein, the online fast fashion giant, has become a global phenomenon, captivating consumers with its vast selection of trendy clothing at incredibly low prices. This success, however, comes at a cost. The company’s rapid production cycle, driven by an intricate network of factories, raises concerns about labor conditions, environmental impact, and ethical sourcing.
Understanding the Shein Production Model:
Shein’s business model relies on a highly efficient and agile production system, characterized by:
- Short Lead Times: Shein prioritizes rapid turnaround times, responding quickly to changing fashion trends and consumer demand. This allows them to introduce new styles frequently, keeping customers engaged and encouraging repeat purchases.
- Just-in-Time Production: The company avoids large-scale inventory by producing garments only after receiving orders. This minimizes risk and allows for greater flexibility in responding to fluctuating market trends.
- Vertical Integration: Shein has a significant degree of control over its supply chain, from design to manufacturing and distribution. This vertical integration allows for streamlined operations and faster decision-making.
- Agile Design and Development: Shein leverages technology to expedite the design and development process. This includes utilizing digital pattern-making, 3D modeling, and rapid prototyping techniques.
- Global Network of Factories: Shein outsources production to a vast network of factories located primarily in China, but also in countries like Bangladesh, Vietnam, and Turkey. This network allows for cost-effective production and access to a diverse range of manufacturing capabilities.
The Challenges and Concerns of Shein’s Production Model:
While Shein’s fast fashion model offers advantages in terms of affordability and speed, it also presents significant challenges:
- Labor Conditions: Reports have surfaced alleging poor working conditions in some of Shein’s factories, including long hours, low wages, and unsafe environments. These concerns highlight the ethical implications of fast fashion production and the need for greater transparency and accountability within the industry.
- Environmental Impact: The rapid production cycle and reliance on synthetic materials contribute to environmental concerns. The production and disposal of fast fashion garments generate significant waste, consume large amounts of water and energy, and release harmful pollutants into the environment.
- Transparency and Traceability: Shein’s complex supply chain and lack of transparency about its sourcing practices make it difficult to verify the conditions under which its products are made. This lack of transparency raises concerns about the potential for exploitation and environmental harm.
- Sustainability Concerns: The fast fashion model, by its very nature, encourages a culture of disposable clothing. This contributes to a cycle of overconsumption and waste, undermining efforts towards sustainable fashion practices.
The Future of Shein’s Production Model:
Shein’s fast fashion model has been criticized for its environmental and social impacts. However, the company has taken some steps to address these concerns, including:
- Sustainability Initiatives: Shein has launched initiatives aimed at reducing its environmental footprint, such as using recycled materials and promoting sustainable packaging.
- Improved Transparency: The company has made efforts to increase transparency by providing information about its supply chain and sourcing practices.
- Collaboration with Industry Partners: Shein has partnered with organizations and industry leaders to promote ethical and sustainable practices within the fast fashion sector.
However, much work remains to be done. Shein needs to commit to more robust sustainability initiatives, increase transparency across its supply chain, and actively engage with stakeholders to address concerns about labor conditions and environmental impact.
FAQs about Shein’s Production Model:
Q: Where are Shein’s factories located?
A: Shein’s factories are primarily located in China, but the company also outsources production to factories in Bangladesh, Vietnam, and Turkey.
Q: What are the working conditions like in Shein’s factories?
A: Reports have surfaced alleging poor working conditions in some of Shein’s factories, including long hours, low wages, and unsafe environments. However, Shein has stated that it is committed to improving working conditions in its supply chain.
Q: How does Shein’s production model impact the environment?
A: The company’s rapid production cycle and reliance on synthetic materials contribute to environmental concerns. The production and disposal of fast fashion garments generate significant waste, consume large amounts of water and energy, and release harmful pollutants into the environment.
Q: What steps is Shein taking to address sustainability concerns?
A: Shein has launched initiatives aimed at reducing its environmental footprint, such as using recycled materials and promoting sustainable packaging. The company has also partnered with organizations and industry leaders to promote ethical and sustainable practices within the fast fashion sector.
Tips for Consumers Regarding Shein’s Products:
- Consider the Environmental Impact: Before purchasing Shein products, consider the environmental impact of fast fashion. Explore alternatives such as buying secondhand clothing, supporting sustainable brands, or reducing overall consumption.
- Research Labor Conditions: Stay informed about the working conditions in Shein’s factories and consider supporting brands that prioritize ethical sourcing and labor practices.
- Choose Sustainable Options: If you do choose to purchase from Shein, opt for products made from sustainable materials or with eco-friendly features.
- Support Transparency: Encourage Shein to increase transparency about its supply chain and sourcing practices.
Conclusion:
Shein’s fast fashion model presents a complex dilemma. While it offers consumers affordable and trendy clothing, it also raises concerns about labor conditions, environmental impact, and ethical sourcing. The company has made some progress in addressing these issues, but significant challenges remain. As consumers, we have a responsibility to be informed about the consequences of our purchasing decisions and to support brands that prioritize ethical and sustainable practices.
The future of fast fashion lies in finding a balance between affordability, style, and sustainability. Shein, and the industry as a whole, must prioritize ethical and environmental considerations to ensure a future where fashion is accessible, desirable, and responsible.
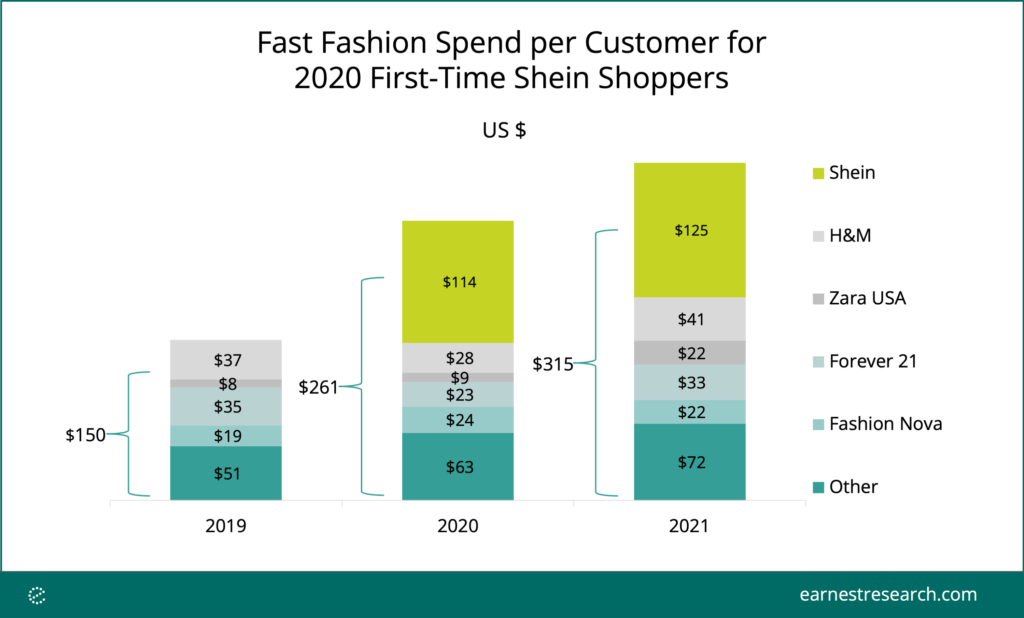


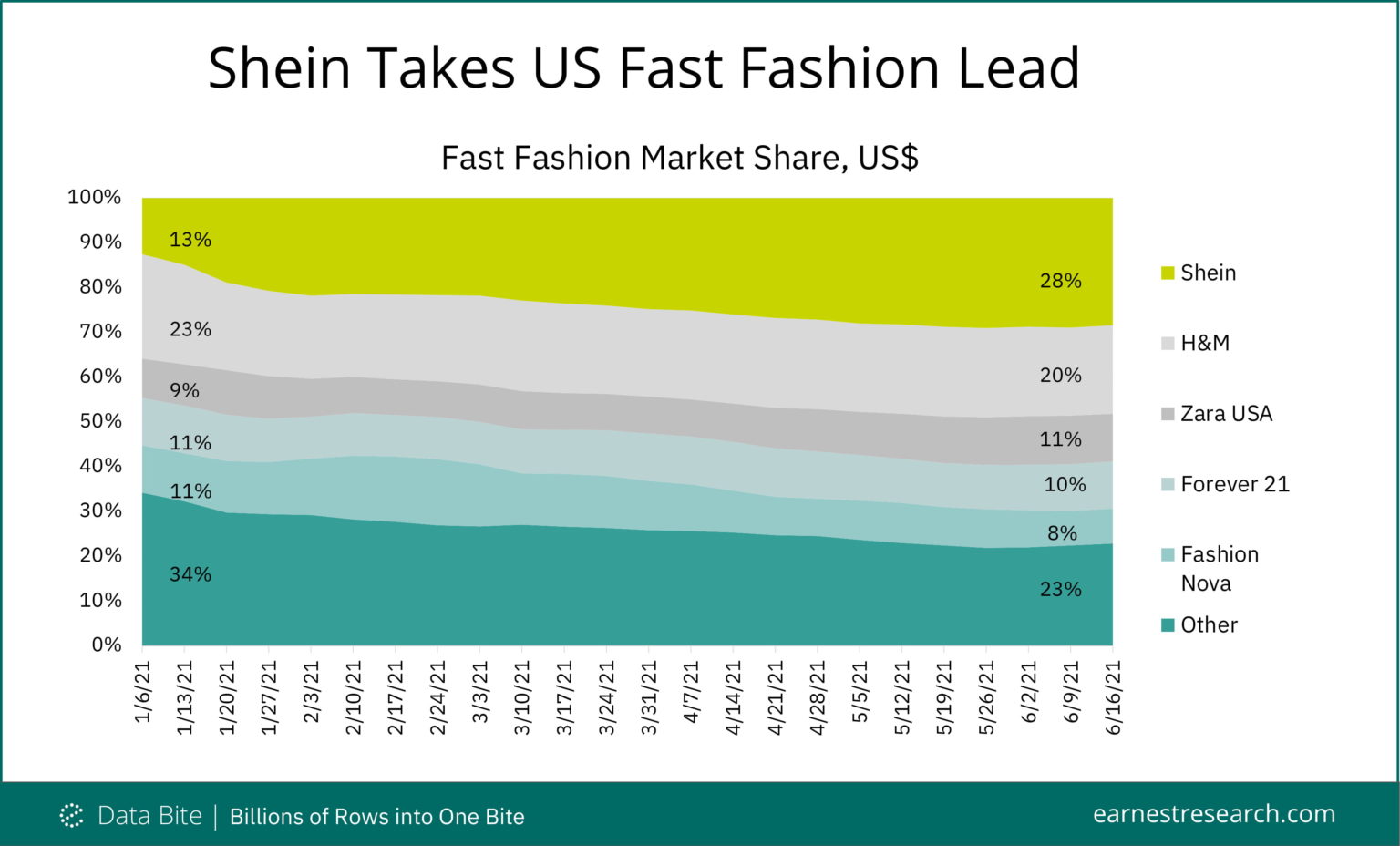

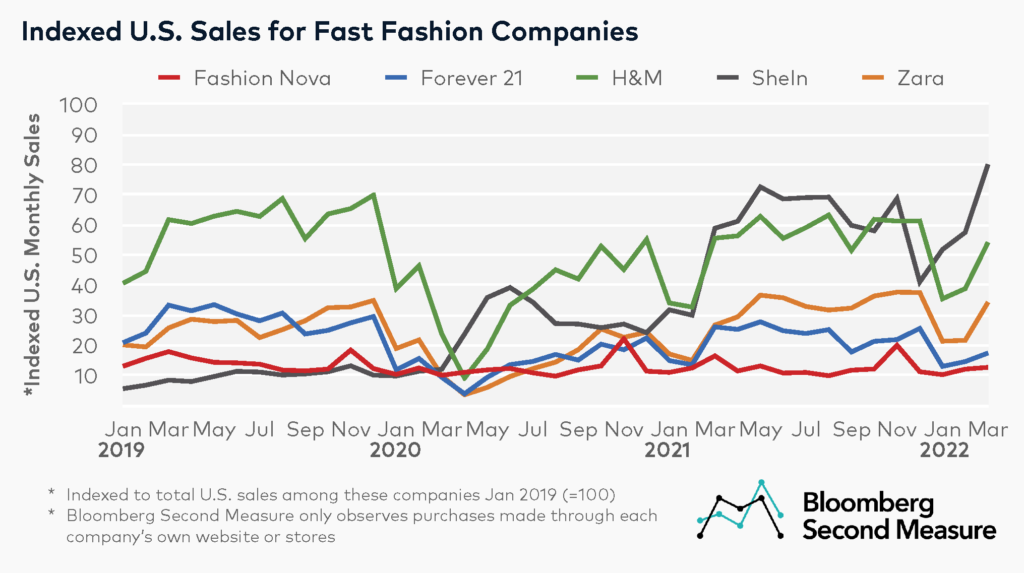


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Shein: A Case Study in Fast Fashion Production. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!